The term data protection refers to actually protecting data while in transit and at rest.
Protecting your data using encryption.
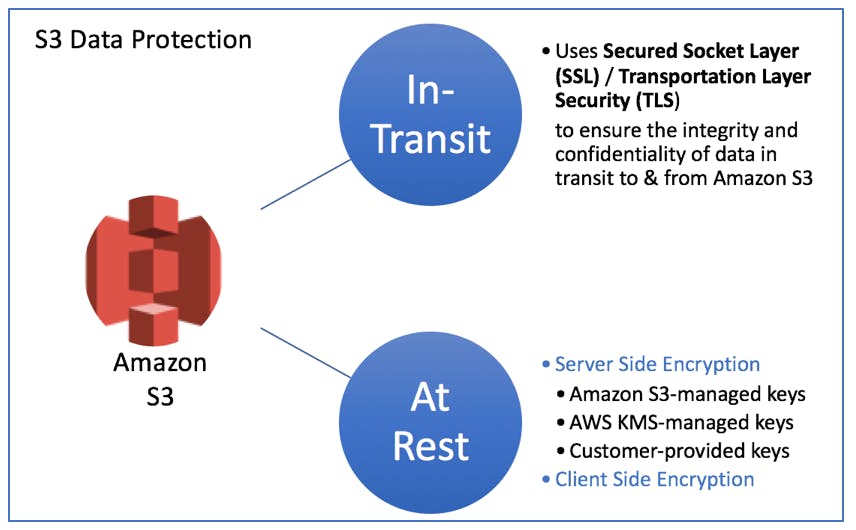
In transit as it travels to and from Amazon S3:
At rest while it is stored on disks in Amazon S3 data centers:
You can protect data in transit using Secure Socket Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) or client-side encryption. You have the following options for protecting data at rest in Amazon S3.
Server-Side Encryption – Request Amazon S3 to encrypt your object before saving it on disks in its data centers and then decrypt it when you download the objects.
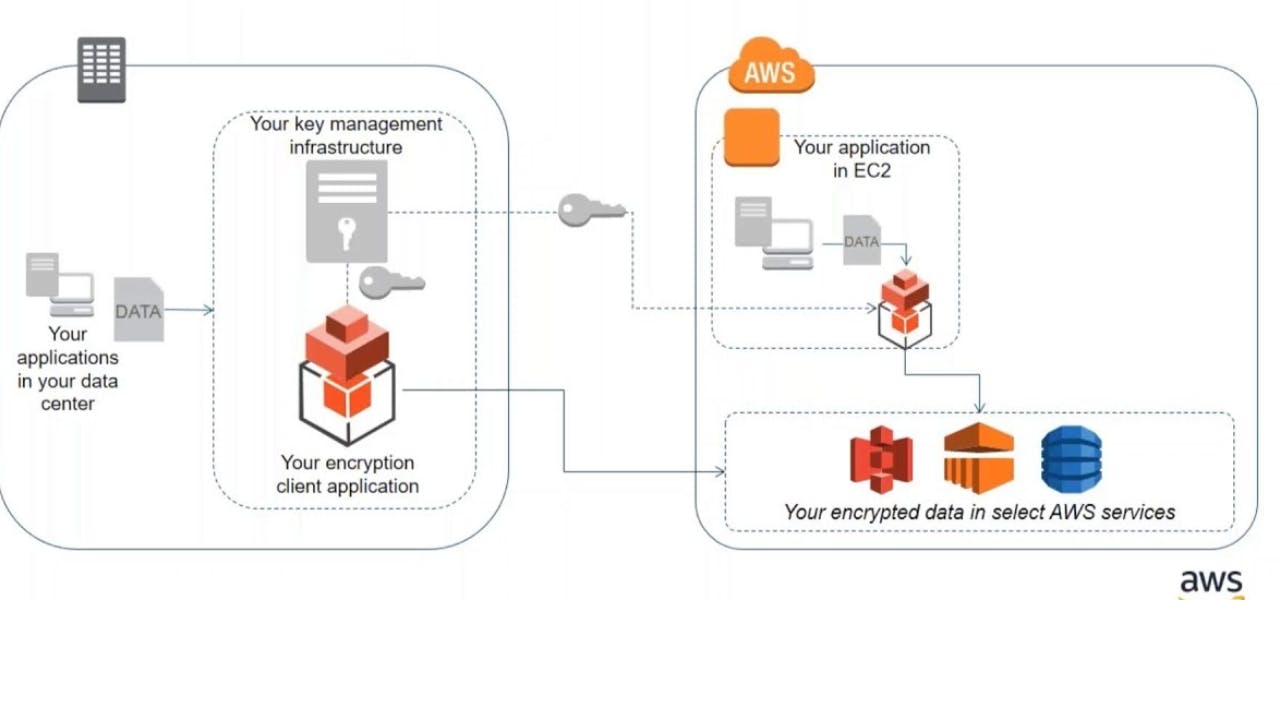
Client-Side Encryption – Encrypt data client-side and upload the encrypted data to Amazon S3. In this case, you manage the encryption process, the encryption keys, and related tools.
Server side encryption options:
SSE-S3 – Server Side Encryption with S3 managed keys
- Each object is encrypted with a unique key.
- Encryption key is encrypted with a master key.
- AWS regularly rotate the master key.
- Uses AES 256.
SSE-KMS – Server Side Encryption with AWS KMS keys
- KMS uses Customer Master Keys (CMKs) to encrypt.
- Can use the automatically created CMK key.
- OR you can select your own key (gives you control for management of keys).
- An envelope key protects your keys.
- Chargeable.
SSE-C – Server Side Encryption with client provided keys
- Client manages the keys, S3 manages encryption.
- AWS does not store the encryption keys.
- If keys are lost data cannot be decrypted.
Client side encryption
You encrypt objects using your own local encryption process before uploading it to S3.
For more information I've attached the aws link below: docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/Usi..
Thanks for reading. I just wanted to post a some quick notes I took to prepare for my Solutions Architect exam. Good Luck.

